How to Build a Faceless Tiktok Channel with AI
Building a faceless video channel is an increasingly popular trend in content creation, especially on platforms like TikTok and YouTube.
Sam
Creator or RVE
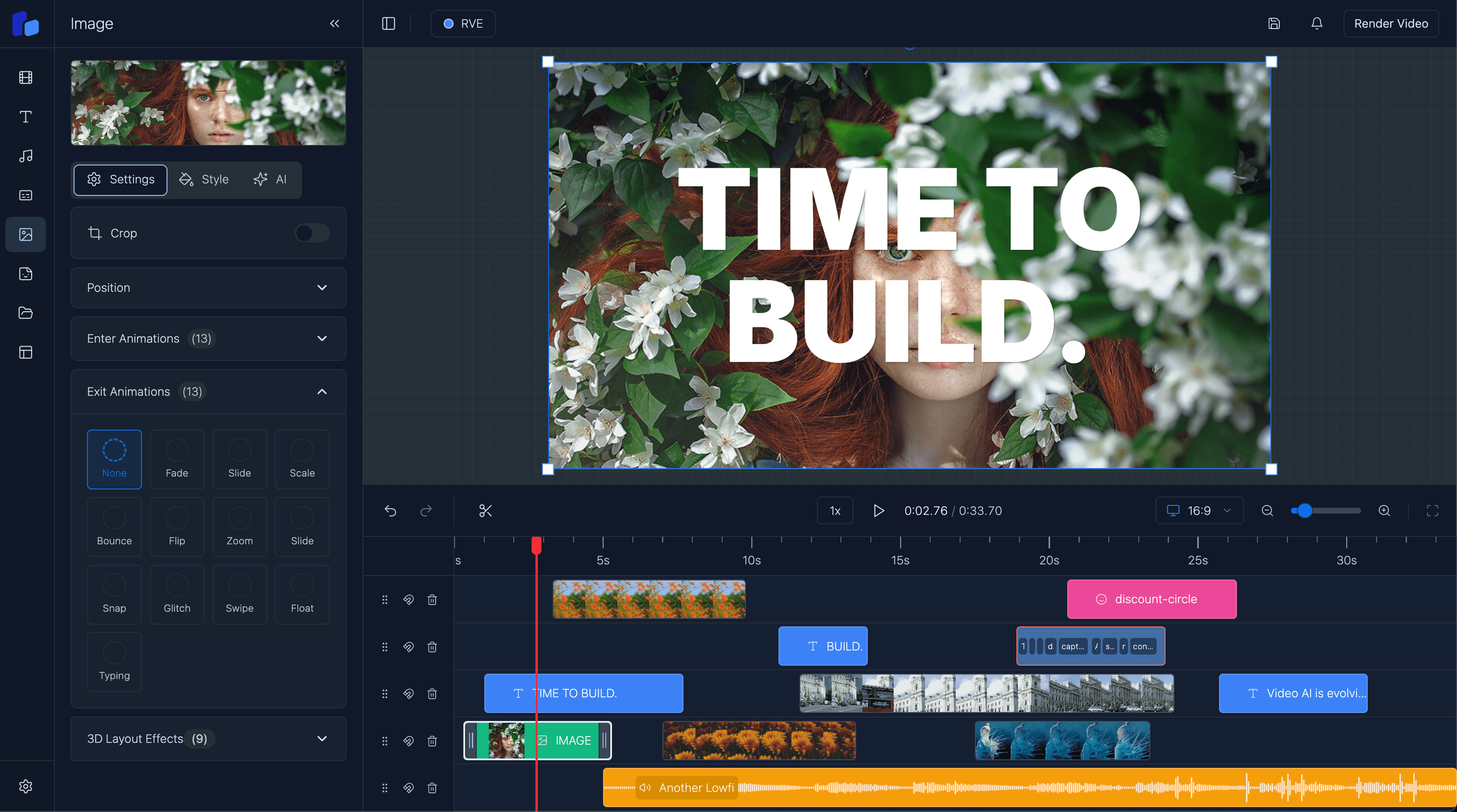
So within Version 6 there are two ways to generate captions at the moment:
I'll break down how the CaptionsPanel works, focusing on its two main input methods: manual text entry and file upload.
Manual Text Entry Method
const generateCaptions = () => {
// Split text into sentences using punctuation
const sentences = script
.split(/[.!?]+/)
.map((sentence) => sentence.trim())
.filter((sentence) => sentence.length > 0);
// Calculate timing based on average reading speed
const wordsPerMinute = 160;
const msPerWord = (60 * 1000) / wordsPerMinute;
let currentStartTime = 0;
const processedCaptions: Caption[] = sentences.map((sentence) => {
const words = sentence.split(/\s+/);
const sentenceStartTime = currentStartTime;
// Create timing for each word
const processedWords = words.map((word, index) => ({
word,
startMs: sentenceStartTime + index * msPerWord,
endMs: sentenceStartTime + (index + 1) * msPerWord,
confidence: 0.99,
}));
// Create caption segment
const caption: Caption = {
text: sentence,
startMs: sentenceStartTime,
endMs: sentenceStartTime + words.length * msPerWord,
timestampMs: null,
confidence: 0.99,
words: processedWords,
};
// Add gap between sentences
currentStartTime = caption.endMs + 500;
return caption;
});
};This code:
- Splits input text into sentences using punctuation
- Estimates timing based on 160 words per minute
- Creates word-level timing data
- Adds small gaps between sentences
- Generates a Caption[] array with timing information
File Upload Method
const handleFileUpload = (event: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
const file = event.target.files?.[0];
if (!file) return;
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = (e) => {
try {
// Parse JSON file
const jsonData = JSON.parse(e.target?.result as string) as WordsFileData;
// Group words into chunks of 5
const processedCaptions: Caption[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < jsonData.words.length; i += 5) {
const wordChunk = jsonData.words.slice(i, i + 5);
const startMs = wordChunk[0].start * 1000;
const endMs = wordChunk[wordChunk.length - 1].end * 1000;
const captionText = wordChunk.map((w) => w.word).join(" ");
processedCaptions.push({
text: captionText,
startMs,
endMs,
timestampMs: null,
confidence: wordChunk.reduce((acc, w) => acc + w.confidence, 0) / wordChunk.length,
words: wordChunk.map((w) => ({
word: w.word,
startMs: w.start * 1000,
endMs: w.end * 1000,
confidence: w.confidence,
})),
});
}
// ... create and add overlay
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to parse file:', error);
}
};
};The upload expects a JSON file with this structure:
interface WordsFileData {
words: {
word: string; // The word text
start: number; // Start time in seconds
end: number; // End time in seconds
confidence: number; // Confidence score (0-1)
}[];
}Example JSON file:
{
"words": [
{
"word": "Hello",
"start": 0.0,
"end": 0.5,
"confidence": 0.98
},
{
"word": "world",
"start": 0.6,
"end": 1.1,
"confidence": 0.95
}
]
}Summary
Both methods ultimately create a CaptionOverlay that:
- Groups words into manageable segments
- Maintains precise timing information
- Includes confidence scores
- Positions the captions on the timeline using findNextAvailablePosition
- Sets default positioning (left: 230, top: 414, width: 833, height: 269)
The key difference is:
- Manual entry: Estimates timing based on average reading speed
- File upload: Uses precise timing from the JSON file, typically from speech recognition
Both methods create the same CaptionOverlay structure, just with different timing precision and confidence scores.